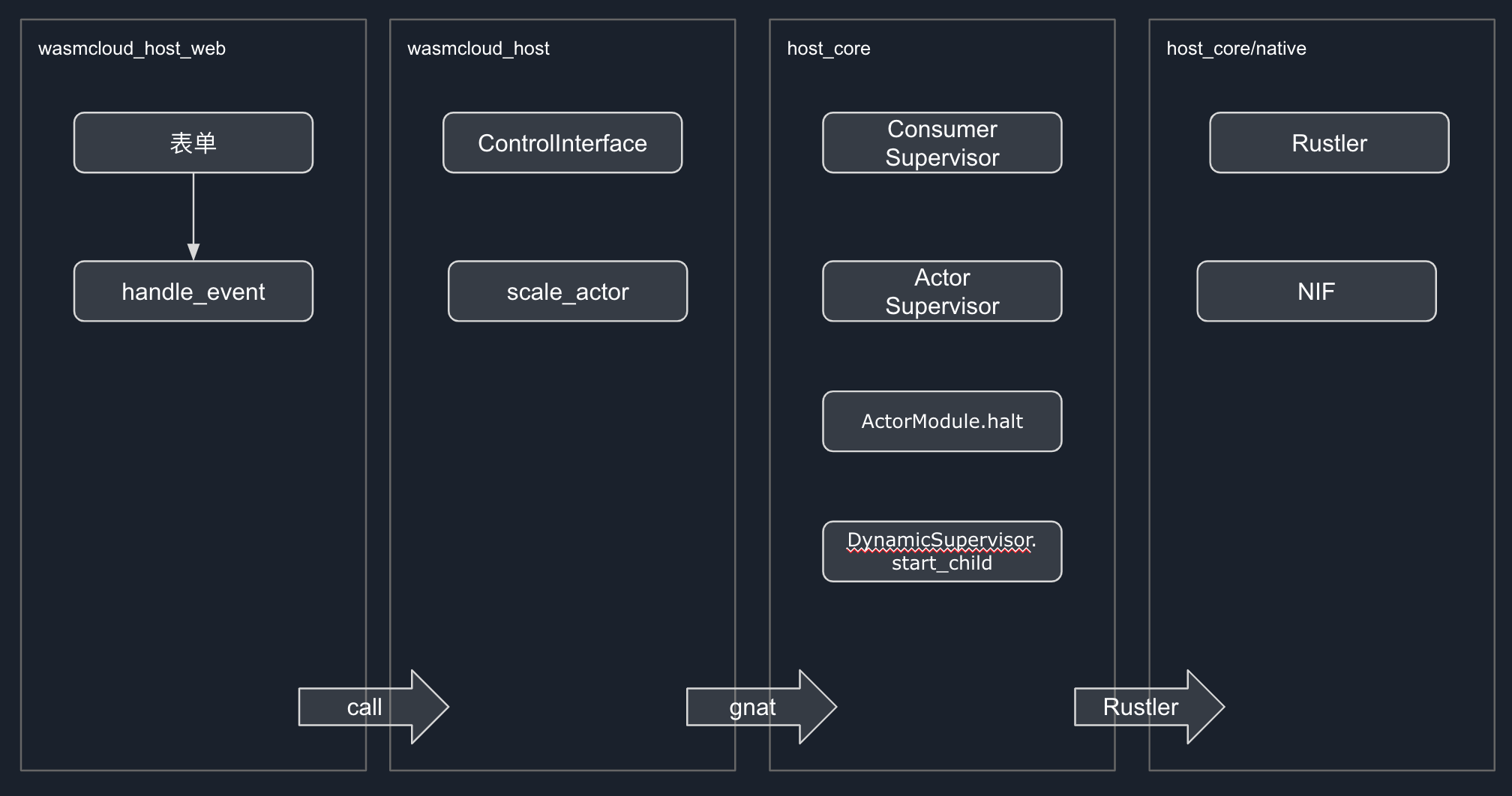
组成
模块
作用
wasmcloud_host_web
Web 平台,由 phoenixframework+liveview 技术栈组成,响应用户的操作。
wasmcloud_host
接收web的操作,包装数据,发送给 nat
host_core
主要负责 nat 消息的处理,actor 进程的直接管理(增删)
host_core/native
执行 actor wasm
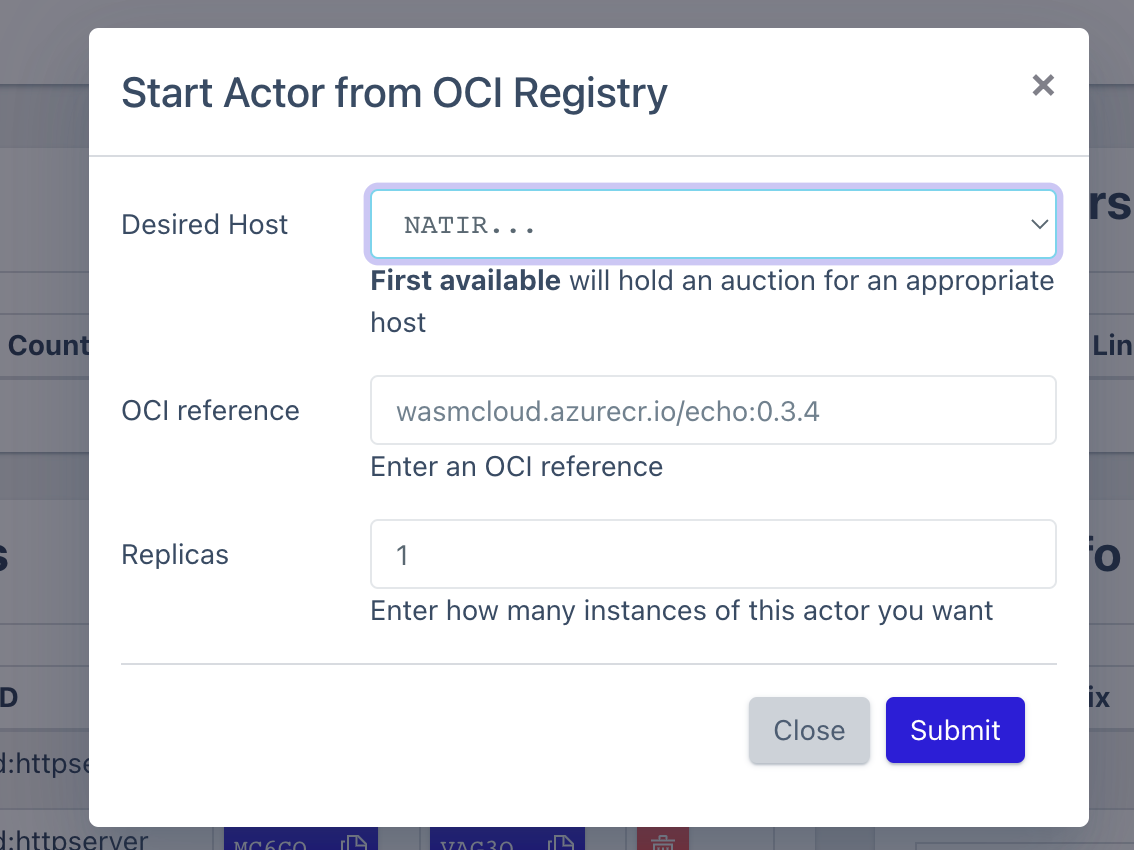
Start actor wasmcloud_host_web (UI) webui 部分使用的是 phoenixframework + liveview 的技术栈来构建。这里重点需要关注的文件是 start_actor_component.ex,在用户点击完 submit 后触发事件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def render do modal_id = case assigns.id do :start_actor_file_modal -> "start_actor_file" ***:start_actor_ociref_modal -> "start_actor_ociref" *** :start_actor_file_hotreload_modal -> "start_actor_file_hotreload" end ~L"" " <form class=" form-horizontal" ***phx-submit=" <%= modal_id %>"*** phx-change=" validate" phx-target=" <%= @myself %>">
重点代码部分已使用斜体加粗表示。
对于示例,会触发 start_actor_ociref 事件,进而被事件处理函数 handle_event(”start_actor_ociref 所匹配。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 def handle_event ***"start_actor_ociref" ,*** %{"count" => count, "actor_ociref" => actor_ociref, "host_id" => host_id}, socket ) do case host_id do "" -> ***host_id -> start_actor(actor_ociref, count, host_id, socket)*** end end defp start_actor do case ***WasmcloudHost.Lattice.ControlInterface.scale_actor***( actor_id, actor_ociref, String.to_integer(count), host_id ) do end end
wasmcloud_host 根据上面的梳理,我们知道在用户提交了相关信息后,最后调用如下(含值):
1 2 3 4 5 6 WasmcloudHost.Lattice.ControlInterface.scale_actor( actor_id = "MBCFOPM6JW2APJLXJD3Z5O4CN7CPYJ2B4FTKLJUR5YR5MITIU7HD3WD5" actor_ociref = "wasmcloud.azurecr.io/echo:0.3.4" desired_count = 1 host_id = "NATIRMKFPZ3C6M3LYJBZUMAP72WCUKIDFVUYW77CC5IMRL5XRMYXXWXM" )
其中 actor_id 可以使用 wash 指令来获得,是 actor 的固有属性之一。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 wash claims inspect wasmcloud.azurecr.io/echo :0.3.4 Echo - Module Account ACOJJN6WUP4ODD75XEBKKTCCUJJCY5ZKQ56XVKYK4BEJWGVAOOQHZMCW Module MBCFOPM6JW2APJLXJD3Z5O4CN7CPYJ2B4FTKLJUR5YR5MITIU7HD3WD5 Expires never Can Be Used immediately Version 0.3.4 (4) Call Alias (Not set ) Capabilities HTTP Server Tags None
其函数的定义在文件 control_interface.ex
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 defmodule WasmcloudHost.Lattice.ControlInterface do @wasmbus_prefix "wasmbus.ctl." def ***scale_actor do ***topic = "#{@wasmbus_prefix } #{HostCore.Host.lattice_prefix()} .cmd.#{host_id} .scale" *** ***payload = Jason.encode!(%{ "actor_id" => actor_id, "actor_ref" => actor_ref, "count" => desired_count })*** ***case ctl_request(topic, payload, 2_000 ) do *** end end defp ctl_request do ***Gnat.request(:control_nats , topic, payload, request_timeout: timeout)*** end
上述函数处理的重点在于包装需要的数据(payload),并通过 nat 进行通信。其中两个重要的参数和值分别如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 topic = "wasmbus.ctl.default.cmd.NBNT7GUJSLQPIZ4LD4VALYXSRRPKWOLNKIC4LRGFOJNFQ43OJTMQ3AIM.scale" payload = { "actor_id" : "MBCFOPM6JW2APJLXJD3Z5O4CN7CPYJ2B4FTKLJUR5YR5MITIU7HD3WD5" , "actor_ref" : "wasmcloud.azurecr.io/echo:0.3.4" , "count" : 1 }
至此,我们已经梳理出用户在 UI 界面中 start actor 时,与 nat 进行交互的 topic 和 payload 内容
host_core 经过上面的梳理,我们看到最后和 nat 交互的信息如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ***Gnat.request(:control_nats , topic =*** "wasmbus.ctl.default.cmd.NBNT7GUJSLQPIZ4LD4VALYXSRRPKWOLNKIC4LRGFOJNFQ43OJTMQ3AIM.scale" ***, payload =*** { "actor_id" : "MBCFOPM6JW2APJLXJD3Z5O4CN7CPYJ2B4FTKLJUR5YR5MITIU7HD3WD5" , "actor_ref" : "wasmcloud.azurecr.io/echo:0.3.4" , "count" : 1 }***, request_timeout: timeout)***
接下来我们需要找到 host_core 中消费该 topic 的进程处理模块。这部分可在 host_core.ex 查阅,其中 Supervisor.start_link 启动守护进程(或叫监督进程)时定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 defp mount_supervisor_tree do [ Supervisor.child_spec( {Gnat.ConsumerSupervisor, %{ ***connection_name: :control_nats , module: HostCore.ControlInterface.Server,*** subscription_topics: [ %{topic: "#{config.ctl_topic_prefix} .#{config.lattice_prefix} .registries.put" }, ***%{ topic: "#{config.ctl_topic_prefix} .#{config.lattice_prefix} .cmd.#{config.host_key} .*" },*** ] }}, id: :latticectl_consumer_supervisor ),
我们可以看出,其 topic 对应的处理模块为 HostCore.ControlInterface.Server,server.ex 文件。其核心代码摘录如下:
其中的 request 为 use Gnat.Server 时的 callback,可参阅文档:
https://hexdocs.pm/gnat/Gnat.Server.html#c:request/1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 defmodule HostCore.ControlInterface.Server do use Gnat.Server def request topic: topic, body: body, reply_to: reply_to} = req) do topic |> String.split("." ) |> List.delete_at(0 ) |> List.delete_at(0 ) |> List.delete_at(0 ) |> List.to_tuple() |> handle_request(body, reply_to) end
经过初步的格式解析,最后匹配的处理函数如下(重点已使用粗体标注):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 defp handle_request "cmd" , host_id, "scale" }***, body, _reply_to) do with {:ok , scale_request} <- Jason.decode(body), case ***HostCore.Actors.ActorSupervisor.scale_actor(actor_id, count, actor_ref)*** do {:error , err} -> end
1 2 3 4 5 ***payload =*** { "actor_id" : "MBCFOPM6JW2APJLXJD3Z5O4CN7CPYJ2B4FTKLJUR5YR5MITIU7HD3WD5" , "actor_ref" : "wasmcloud.azurecr.io/echo:0.3.4" , "count" : 1 }***,***
我们看到,其重点在 ActorSupervisor.scale_actor ** 处理,我们再 actor_supervisor.ex 中找到相关处理函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 def scale_actor "" ) do current_instances = find_actor(public_key) current_count = current_instances |> Enum.count() ociref = cond do oci != "" -> oci current_count >= 1 -> ActorModule.ociref(current_instances |> List.first()) true -> "" end ***diff = current_count - desired_count*** cond do ***diff == 0 ->*** :ok ***diff > 0 ->*** ***terminate_actor(public_key, diff, %{})*** ***diff < 0 && ociref != "" ->*** if String.starts_with?(ociref, "bindle://" ) do start_actor_from_bindle(ociref, abs(diff)) else ***start_actor_from_oci(ociref, abs(diff))*** end diff < 0 -> Tracer.set_status(:error , "Not allowed to scale actor w/out OCI reference" ) {:error , "Scaling actor up without an OCI reference is not currently supported" } end end
其中重点的处理函数如下:
terminate_actor(public_key, diff, %{})start_actor_from_oci(ociref, abs(diff))
其对应的函数定义如下
terminate_actor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 def terminate_actor when count > 0 do actors = Registry.lookup(Registry.ActorRegistry, public_key) |> Enum.filter(fn {pid, _v} -> existing = HostCore.Actors.ActorModule.annotations(pid) Map.merge(existing, annotations) == existing end ) remaining = length(actors) - count actors |> Enum.take(count) |> Enum.map(fn {pid, _v} -> pid end ) ***|> Enum.each(fn pid -> ActorModule.halt(pid) end )*** if remaining <= 0 do HostCore.Actors.ActorRpcSupervisor.stop_rpc_subscriber(public_key) end :ok end def halt do if Process.alive?(pid), do: ***GenServer.call(pid, :halt_and_cleanup )*** end
start_actor_from_oci
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 def start_actor_from_oci 1 , annotations \\ %{}) do Tracer.with_span "Starting Actor from OCI" , kind: :server do creds = HostCore.Host.get_creds(oci) case HostCore.WasmCloud.Native.get_oci_bytes( creds, oci, HostCore.Oci.allow_latest(), HostCore.Oci.allowed_insecure() ) do {:error , err} -> Tracer.add_event("OCI image fetch failed" , reason: "#{inspect(err)} " ) Tracer.set_status(:error , "#{inspect(err)} " ) Logger.error("Failed to download OCI bytes for #{oci} : #{inspect(err)} " , oci_ref: oci) {:error , err} {:ok , bytes} -> Tracer.add_event("OCI image fetched" , byte_size: length(bytes)) ***start_actor(bytes |> IO.iodata_to_binary(), oci, count, annotations)*** end end end def start_actor "" , count \\ 1 , annotations \\ %{}) when is_binary(bytes) do case HostCore.WasmCloud.Native.extract_claims(bytes) do {:ok , claims} -> with %{permitted: true } <- HostCore.Policy.Manager.evaluate_action( %{ publicKey: "" , contractId: "" , linkName: "" , capabilities: [], issuer: "" , issuedOn: "" , expiresAt: DateTime.utc_now() |> DateTime.add(60 ) |> DateTime.to_unix(), expired: false }, %{ publicKey: claims.public_key, issuer: claims.issuer, contractId: nil , linkName: nil }, @start_actor ), false <- other_oci_already_running?(oci, claims.public_key) do case 1 ..count |> Enum.reduce_while([], fn _count, pids -> case ***DynamicSupervisor.start_child***( __MODULE__ , ***{HostCore.Actors.ActorModule, {claims, bytes, oci, annotations}***} ) do end end end
其重点在于 DynamicSupervisor.start_child,
wasm执行 根据上面的 start_actor 梳理,涉及到的核心代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def start_actor_from_oci 1 , annotations \\ %{}) do case ***HostCore.WasmCloud.Native.get_oci_bytes***( creds, oci, HostCore.Oci.allow_latest(), HostCore.Oci.allowed_insecure() ) do ***{:ok , bytes} -> start_actor(bytes |> IO.iodata_to_binary(), oci, count, annotations)***
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def start_actor "" , count \\ 1 , annotations \\ %{}) when is_binary(bytes) do case ***HostCore.WasmCloud.Native.extract_claims(bytes)*** do {:ok , claims} -> ***DynamicSupervisor.start_child***( __MODULE__ , ***{HostCore.Actors.ActorModule, {claims, bytes, oci, annotations}***} )
HostCore.WasmCloud.Native
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 defmodule HostCore.WasmCloud.Native do @moduledoc false ***use Rustler, otp_app: :host_core , crate: :hostcore_wasmcloud_native*** def extract_claims do: error() defp error do: :erlang .nif_error(:nif_not_loaded )
其中用到了 Rustler 库,这个库的作用:Safe Rust bridge for creating Erlang NIF functions
在 native.ex 声明,在 rust 项目中实现,比如 extract_claims(_bytes),在 lib.rs 文件中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #[rustler::nif(schedule = "DirtyIo" )] fn get_oci_bytes creds_override: Option <HashMap<String , String >>, oci_ref: String , allow_latest: bool , allowed_insecure: Vec <String >, ) -> Result <(Atom, Vec <u8 >), Error> { task::TOKIO.block_on(async { let path = match oci::fetch_oci_path(&oci_ref, allow_latest, allowed_insecure, creds_override) .await { Ok (p) => p, Err (e) => return Err (rustler::Error::Term(Box ::new(format! ("{}" , e)))), }; let mut output = Vec ::new(); let mut file = tokio::fs::File::open(path).await.map_err(to_rustler_err)?; file.read_to_end(&mut output) .await .map_err(to_rustler_err)?; Ok ((atoms::ok(), output)) }) }